Whether you’ve dived into crypto or are cautiously observing, the best way to fortify your credit union and the security of your members is with Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), a cybersecurity approach intended to address the security risks faced.
This concept might be known by another name within your organization, or just in the beginning stages of implementation. Regardless of where you are in the process, ZTA means diving into complexity, utilizing your budget, and dedicating time, if your credit union doesn’t already. To achieve success, it’s vital to have engagement and cooperation across the organization from senior leadership all the way to data and system owners.
The Zero Trust Maturity Model represents a gradient of implementation across five pillars, allowing for gradual progress towards optimization. As organizations transition into ZTA, solutions will increasingly rely on automated processes and systems that will fully integrate across pillars.
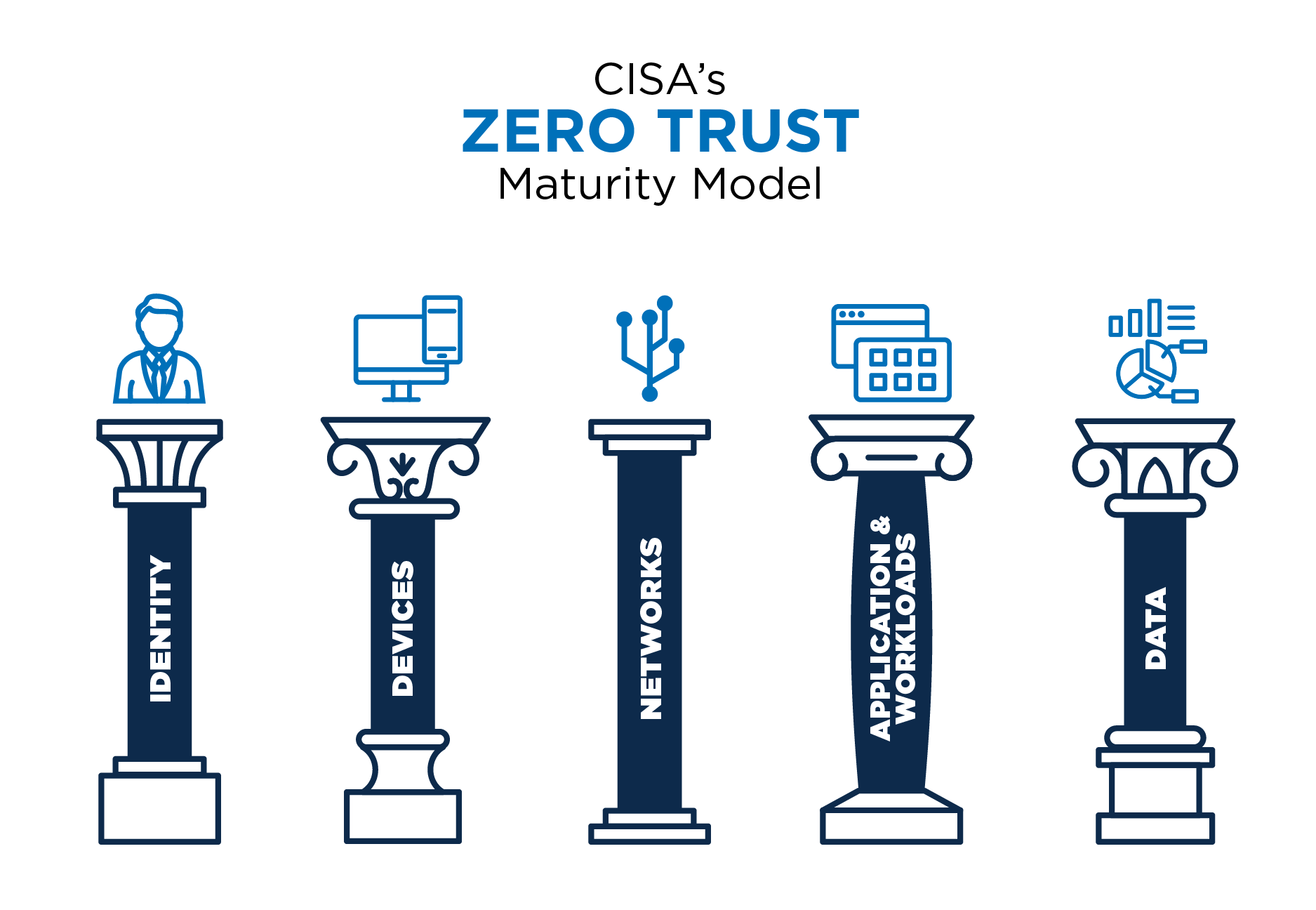
CISA’s Zero Trust Maturity Model (5 pillars)
- Identity – a set of attributes that uniquely identifies an agency user.
- Devices – any asset that can connect to a network.
- Networks – an open communications medium including typical channels such as internal and wireless networks, and the internet.
- Applications and Workloads – agency systems, computer programs, and services that execute on-premises, on mobile devices, and in cloud environments.
- Data – all structured and unstructured files that reside in federal systems, devices, networks, databases, etc.
Drawing back the digital curtain
It’s widely believed that cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum or other forms of digital currency will change the future of global finance. These digital assets are decentralized, independent, and unregulated, operating free of central banks. These features make them both attractive and free of fees. This fact alone presents an excellent opportunity for both companies and individuals to attain wealth, which is also why there’s an increased concern around cybersecurity. For every opportunity to make money, there is an equal, if not greater, desire by bad actors to exploit it.
Decentralization of crypto offers opportunity for cybercriminals to hide their identities, hack into trading platforms, and convert digital currencies into more traditional forms. The criminal opportunity doesn’t stop there however – being a decentralized currency, there’s no fundamental authority monitoring transactions and activities, which provides a haven for criminals.
Having the right cybersecurity in place can protect your credit union and your members from attacks in the future.
Here are the 5 most common cybersecurity risks to watch for:
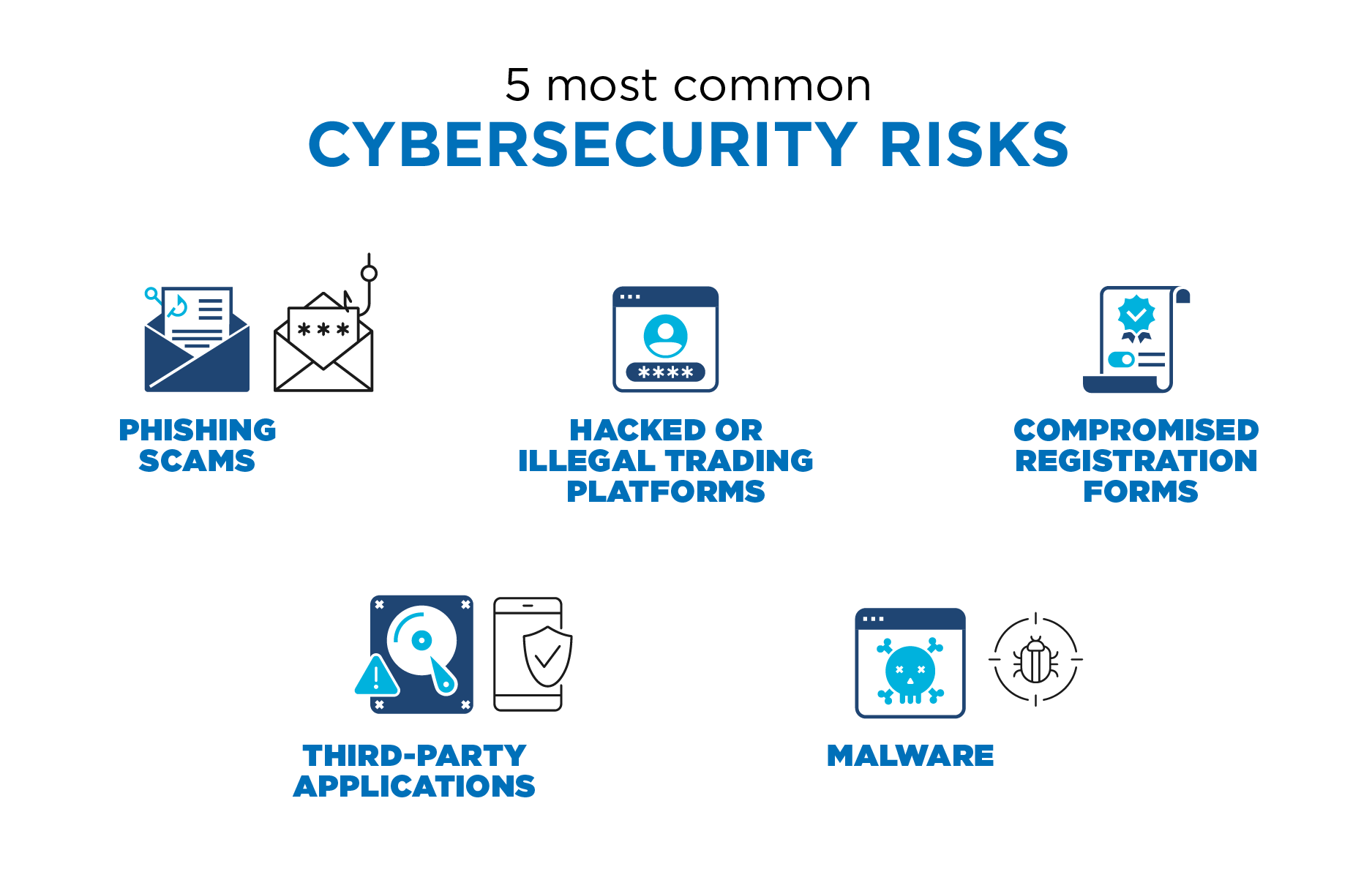
Phishing scams – This technique is used to impersonate a real firm, like a trading platform, and connect with users to convince them to take action, such as clicking on a malicious website.
Hacked or illegal trading platforms – Cybercriminals compromise trading platforms by stealing funds from the users. Because crypto is still new, there are numerous platforms popping up all the time, and not all are trustworthy sites.
Compromised registration forms – Cybercriminals steal users’ information. They then sell it in the black market for profit.
Third-party applications – This is an opportunistic way for cybercriminals to steal user data and use it to target further attacks.
Malware – Crypto-malware allows unauthorized users to mine cryptocurrencies on someone else’s computer. They can compromise or infect a user’s computer by tricking them into installing malicious code, or these criminals will inject malicious code into a site or advertisement.
The current structure of blockchain’s decentralized ecosystem acts as a cybersecurity network. Typically, blockchain reduces exposures, provides strong encryption, and more effectively verifies data ownership and integrity. It can even eliminate the need for some passwords, which has been identified as one of the weakest links in cybersecurity. The principal advantage of blockchain is its use of a distributed ledger.
But how do security breaches happen in such a tech-dominant industry?
It’s the common lack of basic cybersecurity best practices, much like those prescribed in a Zero Trust Architecture, that open the door for security breaches. Again, ZTA is a method used to proactively assess the key components of the rapidity, intricacy, and interruption related to how information or data behave within a network system like blockchain networks. However, this alone doesn’t replace the need or satisfy the requirements for Cyber Liability Insurance.
Cybercrimes will only continue to grow in frequency and level of sophistication, especially with the continuous developments in digital capabilities like cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Cyber Liability requirements are being enforced across the financial sector but not all policy offerings are equal. Your policy should be customized for your credit union and accompanied by the appropriate risk services like on-site risk reviews and on-site training. Cyber Liability is institutional coverage that helps you bounce back by helping to cover associated costs should you fall victim to cybercrimes like that of a potential data breach.
Odds are your credit union won’t actually house the cryptocurrency, but will partner with a third party to transact, store, and sell cryptocurrencies on behalf of your clients. Keep this methodology and legal requirements in mind when looking to partner with a best-in-class provider.
